
MIG/MAG
robotic and manual welding
TIG
welding stainless steel and aluminum
Laser
welding stainless steel and aluminum
Expertise
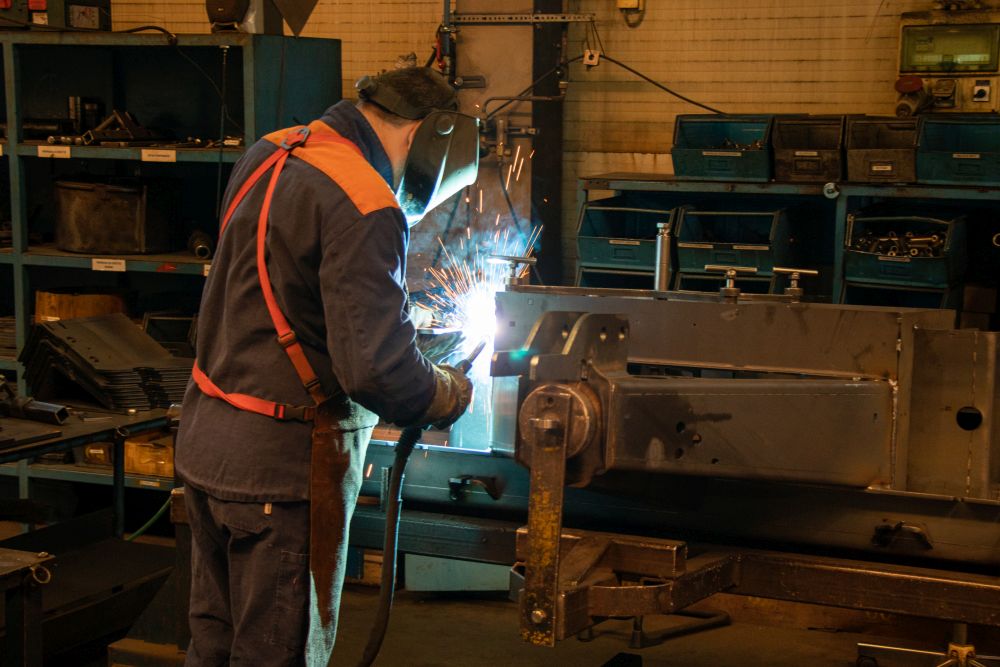
MIG/MAG
MIG/MAG welding (Metal Inert Gas / Metal Active Gas) is a welding process with shielding gas, where a continuously fed wire is used as the electrode. The difference between MIG and MAG lies in the type of gas: inert gas (e.g., argon) for MIG, and active gas (e.g., CO₂-argon mixture) for MAG.
This process is very efficient and suitable for fast welding of larger quantities of material, especially steel, aluminum, and non-ferrous metals. Due to easier operation and high productivity, MIG/MAG is one of the most commonly used welding processes in the industry.


Automation
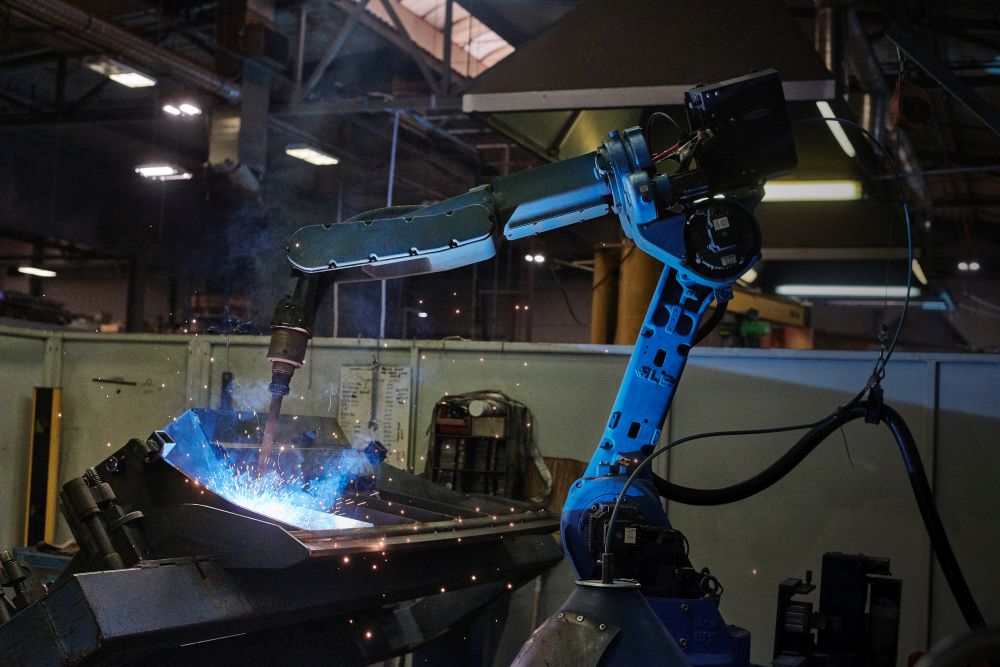
Robotic Welding
Robotic welding is a modern form of automation, enabling fast, precise, and reliable metal welding with industrial robots. It is mainly used in series production, where it ensures consistent quality, higher productivity, and greater safety at work. Ideal for the automotive, metal, and other industries requiring efficiency and repeatability.
Precision
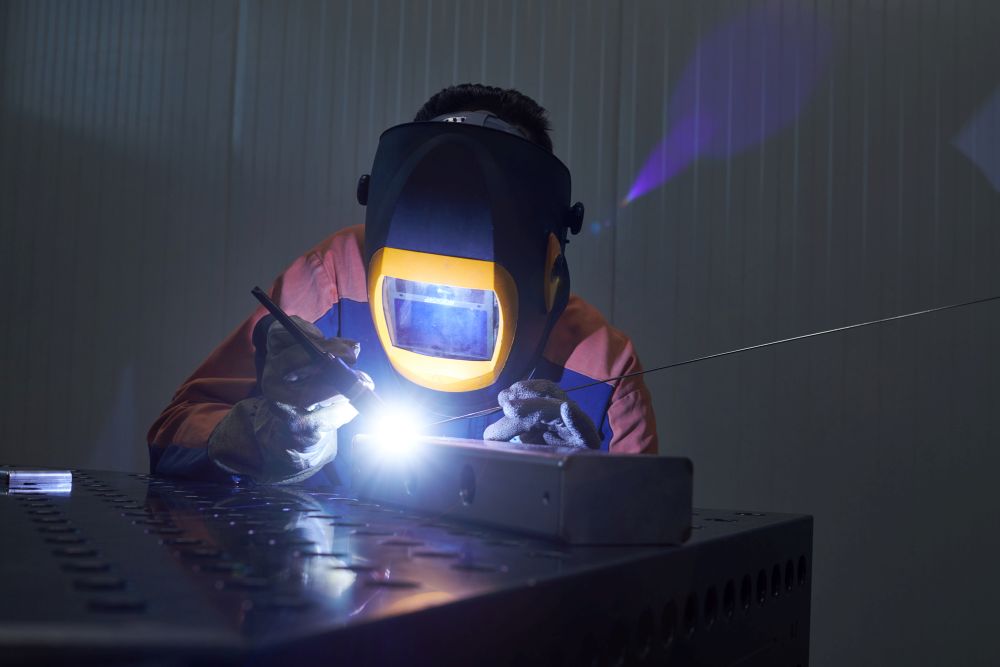
TIG
TIG welding (Tungsten Inert Gas) is a precise welding process using a non-consumable tungsten electrode and inert gas (most often argon) to protect the weld area from oxidation. It enables extremely clean, strong, and aesthetically refined welds, commonly used for stainless steel, aluminum, and thin materials. TIG welding requires high skill, as the welder manually adds filler material and controls the arc, but delivers top-quality results.


Technology
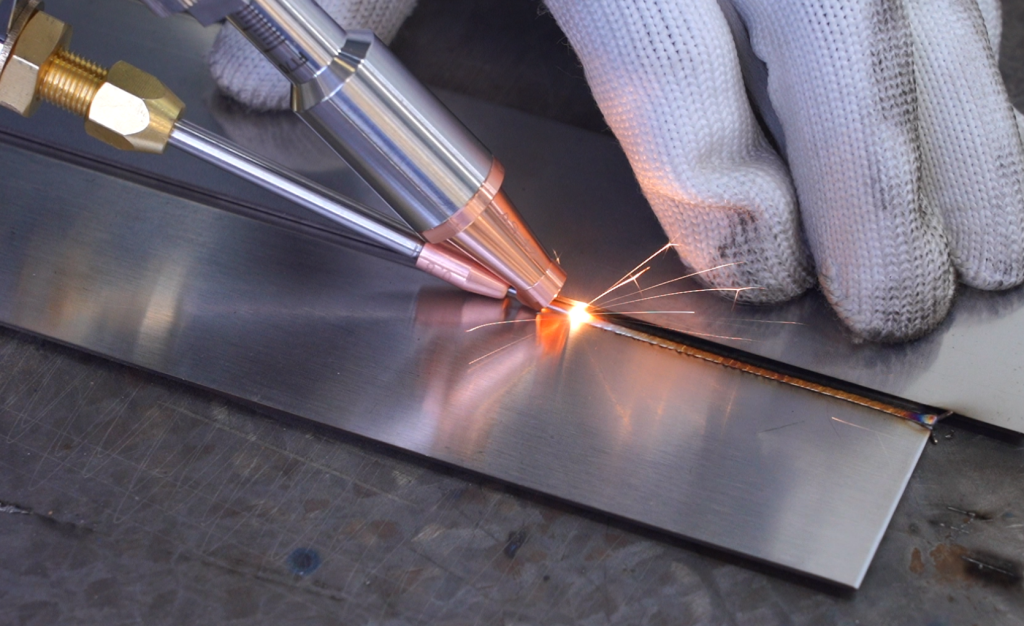
Laser Welding
Laser welding is a high-tech process using a powerful laser beam to precisely join materials. Due to the extremely concentrated thermal energy, it enables very narrow, deep, and clean welds with minimal heat impact on the surrounding material. This reduces deformation and makes it possible to weld very thin or demanding components.
